ご挨拶
放射線治療は小児から超高齢者まで外来で治療できる低侵襲治療が特長です。特に最近では強度変調放射線治療(IMRT)などの、腫瘍だけに正確に当てる新しい技術が開発されました。そのため治癒率が上がると共に副作用もさらに少なくなっています。しかし最も大事なのは機械でなく心です。当科では、悪性腫瘍を中心とする多彩な疾患に対し、偏ることなく内外の最新の知識に基づく治療を行うことを目指しています。初めての治療には不安も多いと思いますが、医師(放射線腫瘍医)と共にきめ細かいケアをおこなう看護師、治療を直接担当する放射線治療技師、また全体的な品質管理に関わる医学物理士や診療を補助する医療秘書、受付事務など全スタッフがそれぞれプロフェッショナルとして患者さんが快適に最善の治療を受けられるよう努めますので安心して受診されてください。
放射線治療科 診療科長
菅原 章友
放射線治療のご案内
当院では放射線治療医師(放射線腫瘍医)と共にきめ細かいケアをおこなう看護師、治療を直接担当する診療放射線技師、また全体的な品質管理に関わる医学物理士や診療を補助する医療秘書、受付事務など全スタッフがそれぞれプロフェッショナルとして患者さんが快適に最善の治療が受けられるよう努めております。
※YouTubeにリンクしています。
診療内容
放射線治療の特徴は、がんのみを死滅させ周囲の正常組織を温存できることです。特に最近では局所に限局しピンポイントに照射する定位放射線治療(SRT)や、腫瘍の形に完全に一致させて照射する強度変調放射線治療(IMRT)により、正常組織の障害はさらに少なくなり、腫瘍への線量増加が可能となり、治癒率がさらに高まっています。多くの部位で手術と同等の治療効果が得られています。がんの種類や病期によっては抗がん剤や手術との併用がよい場合もあります。放射線治療だけの場合には原則的に外来での治療が可能です。身体への負担が少ないため、高齢の患者さんでも安心して治療を受けることができます。日本では放射線治療の普及度が低く、全がん患者の1/4程度が放射線治療を受けるのみですが、欧米では6 割以上が受けており、今後日本でも増加するものと思われます。セカンドオピニオンも受け入れていますので、ご相談ください。一般的な外部照射はライナックという装置を用いて数週間をかけて治療しますが、定位放射線治療では1 回または数回での治療も可能です。2017年より治療装置を増強し、IMRTの進化形である強度変調回転放射線治療(VMAT)による高精度かつ短時間の照射を積極的に行っています。また寡分割照射を推進し通院期間の短縮に努めています。小線源治療は、イリジウム線源を備えたRemote After Loading System(RALS)を用いて画像誘導下に施行しています。2024年に治療とCT撮像を同室でおこなえる装置を導入し、従来より安全で正確な治療が可能になっています。各診療科と連携しながら、個々の患者さんに最も適した治療法を安全に提供できるように努めています。なお、2018年よりJCOG放射線治療グループに加入し症例を登録しています。
主な対象疾患
-
脳腫瘍:グリオーマ、胚芽腫、脳転移など、IMRTや定位放射線治療を施行。
-
頭頸部腫瘍:喉頭癌、咽頭癌、口腔癌などに根治的照射、術後照射を照射単独または化学放射線療法。主にIMRTを施行。
-
肺癌:早期肺癌は定位放射線治療で高齢者でも手術に劣らない成績が得られる。局所進行癌に対しては化学放射線治療を施行。
-
食道癌:根治、術後照射、術後再発に照射単独または化学放射線治療。IMRTも施行。
-
乳癌:乳房温存術後の乳房照射により、局所再発率を約1/3に低下。寡分割(短期)照射を推進。左側乳房癌に対しては長期心毒性の軽減を目指し呼吸気息止照射を導入。
-
肝細胞癌:手術や穿刺療法が適応とならない症例に対して定位放射線治療を施行。
-
直腸癌:中下部直腸癌に対して術前化学放射線治療を施行。
-
婦人科腫瘍:子宮頸癌はⅠ、Ⅱ期でも腔内照射併用で手術と匹敵する治療成績が得られ、標準治療の一つIMRTと画像誘導小線源治療(IGBT)により高精度に最適な治療を施行。
-
前立腺癌:IMRTそ施行。寡分割(短期)照射や定位放射線治療により通院負担を軽減。
-
白血病:造血幹細胞移植の前処置として全身照射を施行。
-
良性疾患:甲状腺眼症、難治性ケロイドなど
-
骨転移など緩和:短期照射を施行。臨床試験として骨転移に対する定位放射線治療も施行
-
その他:さまざまな疾患が対象となりますので、お気軽にお問合せください。
主な診療実績
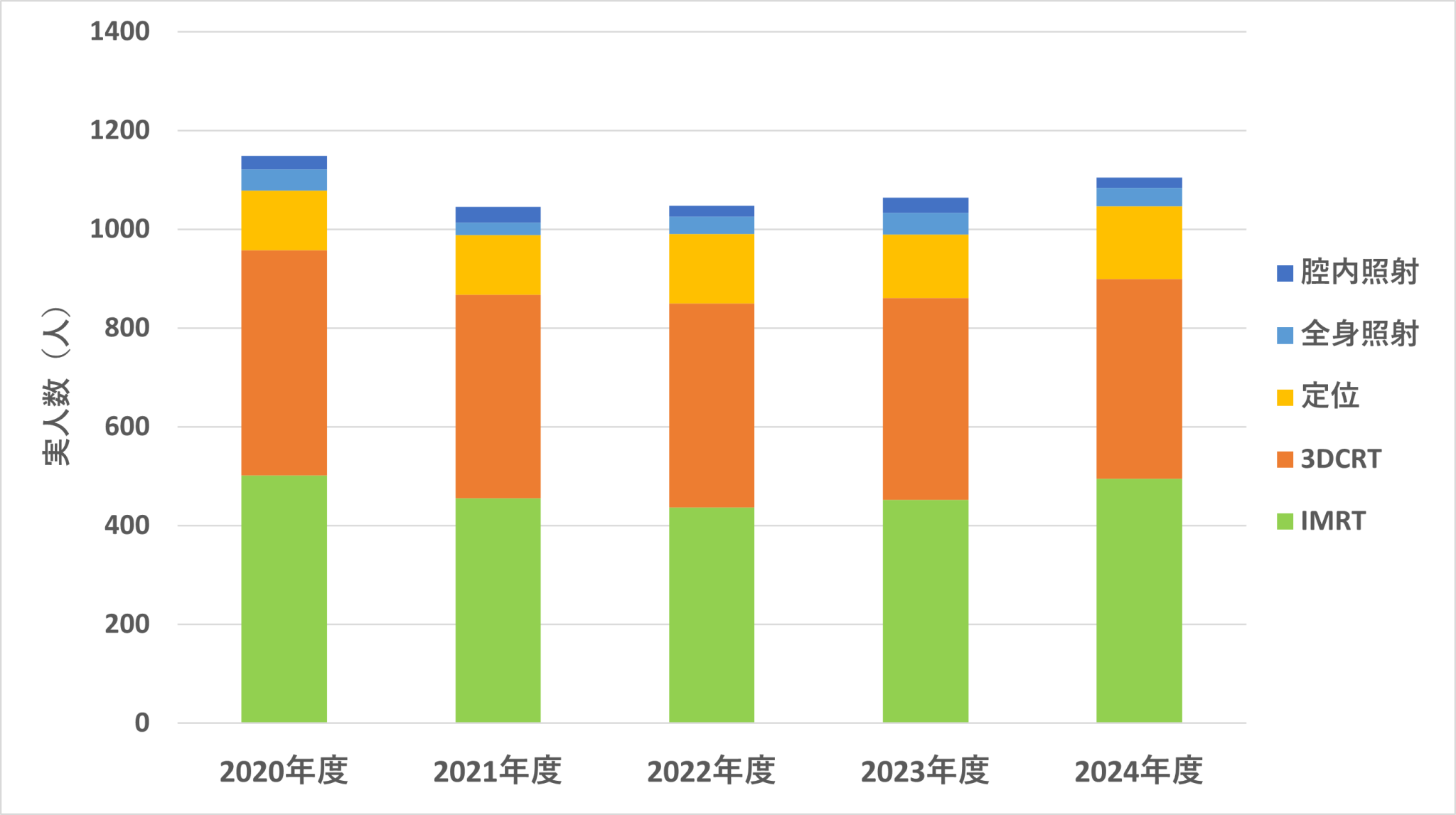
年間症例数は、1995年には350人でしたが年々増加し、最近では年間約 1000人程度と全国有数の症例数です。
2023年の実績:子宮腔内照射31件、3DCRT 409件、IMRT 496件、定位放射線治療128件、全身照射44件など、多くのIMRTや定位放射線治療を施行しています。
2024年実績
子宮腔内照射:21 3DCRT:404 IMRT:495 定位:148 全身照射:37
2023年実績
子宮腔内照射:31 3DCRT:409 IMRT:452 定位:128 全身照射:44
放射線治療の流れ
各科および他院からの紹介で受診
主治医の先生から紹介されての受診となります。
他院からの紹介の場合には紹介状、レントゲン、CTなどの検査結果を持参してください。

診察
診察を行い、これまでの検査結果から病気の種類、部位、進行度などを考慮して最適な治療方法について検討します。放射線治療を行うことが最適であるか、治療の方法はどうするかを検討します。
予測される治療の効果、副作用について説明をし、治療を希望された場合治療計画を立てます。 疑問点があったら納得できるまで質問してください。
患者さんは基本的に放射線治療について深い知識が無いことが多いのでどんな質問でも結構です。遠慮せずに聞いてください。

治療計画
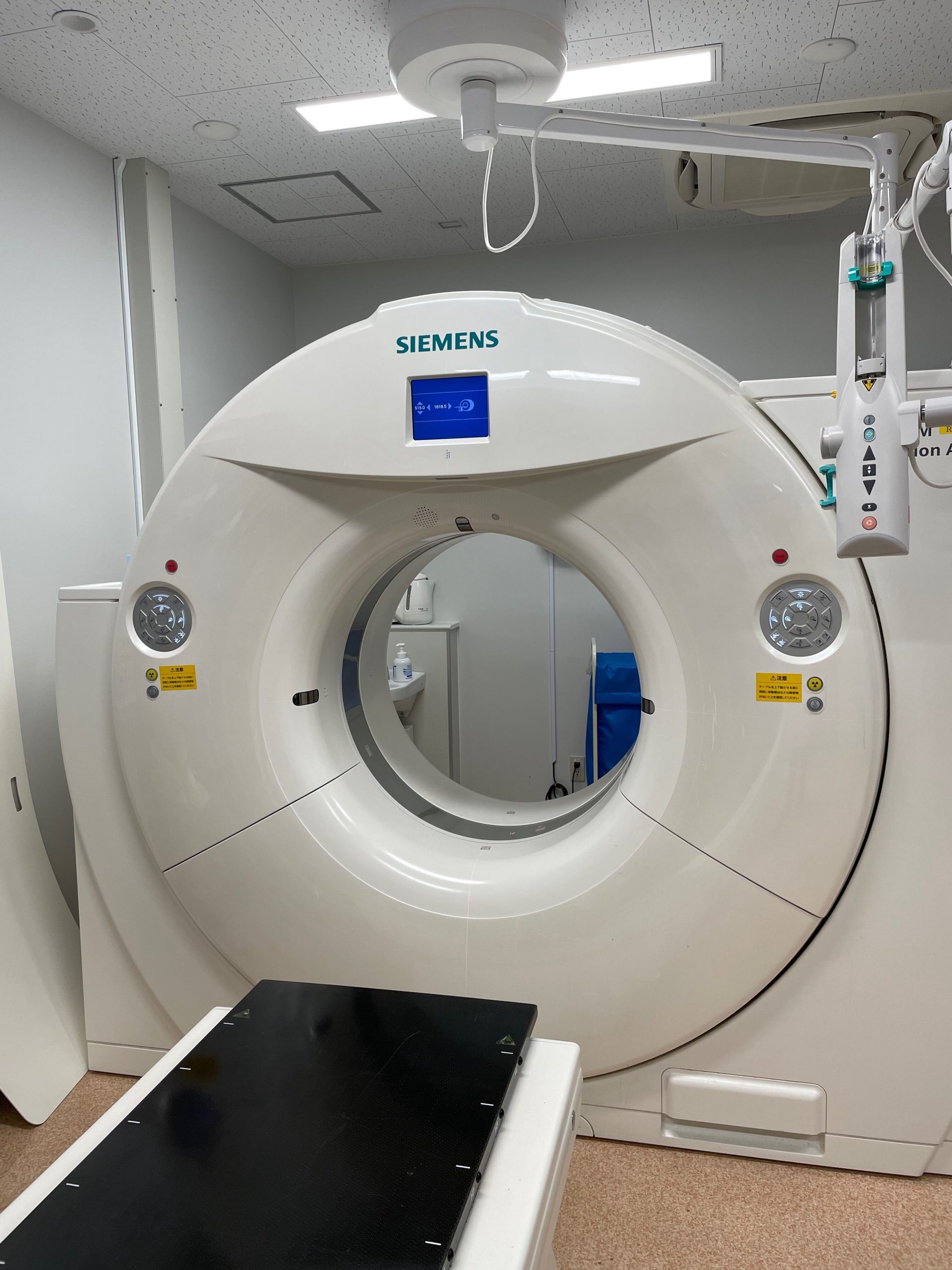
放射線治療をする事にご納得いただいた後、最適と思われる放射線治療の方法を決定します。実際の治療と同様にどの部位に限局して当てるかを決定し体に目印(皮膚に黒いマジックインクで線を書きます)を付ける作業をします。 この作業のことをシミュレーションと呼びます。
目印を付ける際に透視で位置確認をして、レントゲン写真を撮ります。その後CTを撮影します。これは放射線をどの様にかけるか、病気の部分と正常な部分の線量がどの位になるか、という計算を行う時に必要になります。
目印を付ける一連の作業におよそ20~30分程度かかります。
治療
基本的に治療計画を立てた翌々日からの治療となります。
治療計画に基づいて、毎日の治療を行います。一日当たりの治療時間は約5~10分程度です。 (治療部位数、使用機械が複数になる場合はそれ以上時間がかかる場合があります)
基本的には毎週月曜日から金曜日までの週5回の治療を数週間行います。
治療計画の際に付けた目印に従って放射線を照射しますので、印を消さないようにして下さい。
治療時に診察がありますので、何か分からないことや疑問、不安なことがあったらすぐに相談してください。
治療は通院でも可能な場合があります。入院が必要となるのは手術直後、点滴治療を併用している、治療による副作用が強い場合あるいは遠方で通院が不可能な場合です。現在治療している患者さんの60%程度が外来通院で行っています。
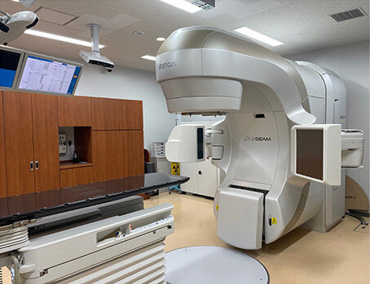
治療室 ①
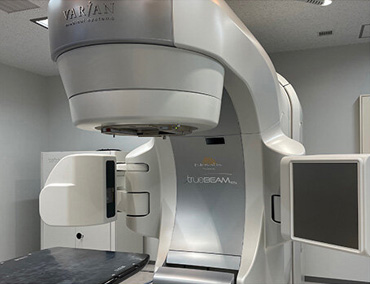
治療室 ②

治療待合室の風景
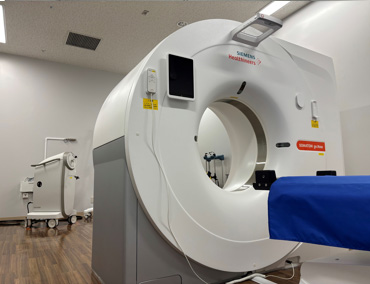
小線源治療室(RALS同室CT)
再診
放射線治療が終了した後も定期的に診察を行います。
必要に応じて各種の検査を行い、治療効果の判定を行います。
また、副作用などについても調査、対処をしています。
基本的に元の診療科と同一の診察日になるようにしています。当科では診察日の変更は電話連絡でも可能です。予約なしに来院された場合、手配のために待ち時間が長くなりますので、必ず事前に連絡をして下さい。
医師一覧
診療科長:菅原 章友
外来:0463(93)1121 内線6641(外来受付)
菅原 章友(すがわら あきとも)教授
| 専門分野 | 放射線治療 |
|---|---|
| 専門医 | 放射線治療専門医 |
| 特に専門とする領域 | 前立腺癌、高精度放射線治療 |
| 外来診療日 | 火曜日・水曜日・金曜日 |
福澤 毅(ふくざわ つよし)講師
| 専門分野 | 放射線治療 |
|---|---|
| 専門医 | 放射線治療専門医 |
| 特に専門とする領域 | 頭頚部腫瘍、食道癌、肺癌、縦隔腫瘍、緩和照射 |
| 外来診療日 | 月曜日・木曜日・金曜日・土曜日 |
黒木 俊寿(くろき としひさ)講師
| 専門分野 | 放射線治療 |
|---|---|
| 専門医 | 放射線治療専門医 |
| 特に専門とする領域 | 肺癌、脳腫瘍、前立腺癌 |
| 外来診療日 | 火曜日・木曜日・金曜日・土曜日 |
三上 達也(みかみ たつや)助教
| 専門分野 | 放射線治療 |
|---|---|
| 専門医 | 放射線科専門医 |
| 特に専門とする領域 | 乳癌、前立腺癌 |
| 外来診療日 | 月曜日・水曜日・木曜日・土曜日 |
豊田 裕理(とよだ ゆうり)助教
| 専門分野 | 放射線治療 |
|---|---|
| 特に専門とする領域 | 各種領域悪性腫瘍 |
| 外来診療日 | 月曜日・火曜日・水曜日・土曜日 |
福本 鴻一(ふくもと こういち)臨床助手
| 専門分野 | 放射線治療 |
|---|---|
| 特に専門とする領域 | 各種領域悪性腫瘍 |
| 外来診療日 | 水曜日・木曜日・金曜日・土曜日 |


